Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
GW IT is implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to enhance security and compliance. RBAC is an access control model that grants permissions to specific roles within a school or department, rather than to individual users. These roles are defined based on job functions and the level of access required to fulfill job responsibilities. By assigning permissions to roles, we can ensure that users only have the access they need to perform their jobs, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Following the successful Spring 2024 pilot with Human Resource Management and Development (HR), we are taking a phased approach to expand the implementation of RBAC. We will engage our campus partners to communicate the initiative, establish timelines and ensure testing, adoption and compliance. Updates about the progress and provide additional details as information becomes available.
RBAC Implementation Process
- Promote
- Introduces the concept and benefits of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC).
- Inventory
- Conduct an audit of current user access to identify any inconsistencies, redundant permissions, or potential security risks.
- Role Mining
- Analyze inventory data to identify common permission patterns and create roles that group similar permissions.
- Configure
- Assign the appropriate permissions to each defined role by configuring the system.
- Go Live
- Conduct a simulation phase to test user access and verify correct configuration, followed by a support phase after going live.
RBAC Implementation Progress
We are using a phased approach to evaluate enterprise systems for Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) implementation. As part of this process, we are partnering with departments and stakeholders to coordinate efforts and ensure a smooth rollout.
Phase 1 (Current Phase) - RBAC for Banner
We are using a phased approach to evaluate enterprise systems for Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) implementation. As part of this process, we are partnering with departments and stakeholders to coordinate efforts and ensure a smooth rollout.
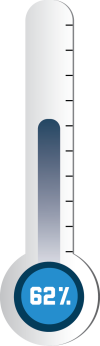
Completed RBAC Implementation for Banner Access
- HRIS
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Enrollment Management
- Med Admissions
- GCAS
- Student Accounts Office
- Law Admissions
- Registrar
- International Student Office
- IT Enterprise Apps
- IT IAM
- IT Service Management
- IT Platforms & Cloud Computing
RBAC for Banner Timeline
The timeline outlines planned RBAC implementations by department. We will continue working closely with campus partners to coordinate these efforts and will share updates as progress continues.
Fall 2025
- Faculty Affairs
- Student Employment
- Budget Office
Winter 2025
- OGSAF
- Controller/Financial Reporting
- Financial Aid
RBAC in Action
RBAC Key Components
Roles
These are defined based on job functions within an organization. For example, roles could be “Admin,” “Editor,” “Viewer,” etc.
Permissions
These are the actions that can be performed within the system, such as “read,” “write,” “delete,” etc.
Users
These are the individuals who need access to the system. Each user is assigned one or more roles.
How it Works
Define Roles
Determine the different roles needed in the organization and what permissions each role should have.
Assign Permissions to Roles
Assign the necessary permissions to each role.
Assign Roles to Users
Assign users to the appropriate roles based on the level of data access required.
Example
Enabling role based access control for a document management system may include the following roles and permissions:
Admin: Can create, read, update, and delete any document.
Editor: Can create and update documents but cannot delete them.
Viewer: Can only read documents.
In this system, if a new employee joins as a content writer, they might be assigned the “Editor” role, giving them the permissions needed to do their job without granting unnecessary access.
Benefits & Applications of RBAC
Key advantages of RBAC is that it simplifies the management of user permissions. Instead of manually assigning permissions to each user, administrators can simply assign users to roles, and the system will automatically grant the appropriate permissions.
RBAC also ensures that access to sensitive information, including GW Restricted Data (e.g., PII, sensitive financial data), is granted only to individuals whose job responsibilities require it.
In addition to its benefits, the following examples illustrate the practical applications and impacts of RBAC:
- Improved User Experience: A new employee joins the university as a Financial Aid counselor. Instead of waiting for an administrator to manually grant them access to the necessary systems, their account is automatically assigned the permissions associated with the Financial Aid Counselor role, allowing them to start working immediately.
- Enhanced Security: A staff member attempts to access student financial records that they are not authorized to view. The RBAC system blocks the access attempt, as their role does not have permissions to view this sensitive data.
- Simplified Management: The university needs to update the permissions for all employees who work in student accounts. Instead of updating individual user accounts, the administrator can simply modify the permissions associated with the Student Account roles, and the changes will be applied automatically.
Questions & Feedback
- If you have questions or feedback about this change, please share them with us by submitting the technology feedback form, and a member of the project team will be in contact with you.



